Detecting Malvertising: Which Tools and Techniques Could Help You With It

The COVID-19 pandemic has presented new opportunities for cybercriminals, and malvertising has not been an exception. With lockdowns, social distancing measures, and remote work becoming the norm, people have spent more time online for work, communication, entertainment, and shopping. This expanded online presence has provided cybercriminals with a larger and more diverse pool of potential targets.
Security researchers and organizations have been working diligently to counter this surge in malicious advertisements. They continuously discover and track thousands of new harmful advertisements every day to protect users and organizations from this.
But it's also crucial for individuals and businesses to remain vigilant, keep their software up to date, use security tools, and follow best practices for online security to minimize the risks associated with malvertising and other cybersecurity threats during these challenging times. How can we do it? Let's analyze it together.
What is malvertising?
Malvertising — or malicious advertising — is a cyberattack technique that injects malicious code within digital ads. These deceptive ads are displayed to users, leading them to unsafe destinations. The embedded malicious code often redirects users to harmful websites, risking their online security.
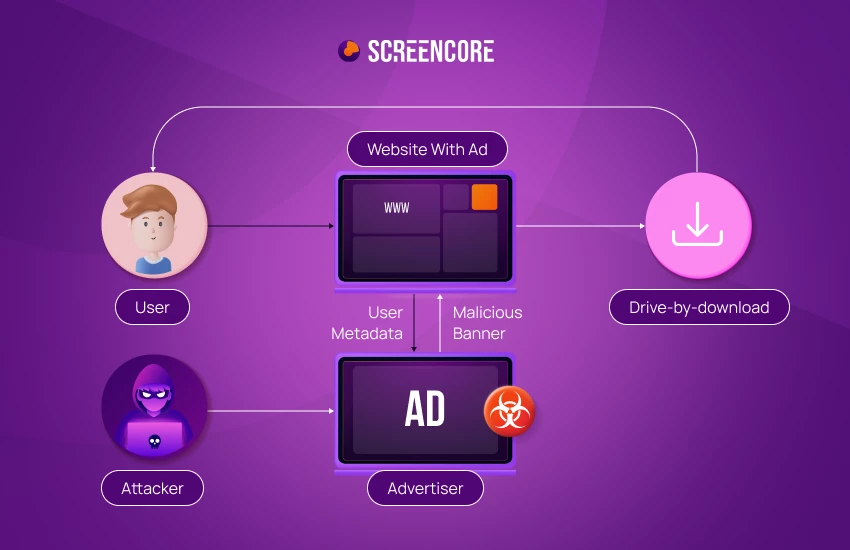
Malvertising can be difficult to detect by both internet users and publishers. These infected ads are usually served to consumers through legitimate advertising networks.
Malvertising can appear on any advertisement on any site, even the ones you visit as part of your everyday Internet browsing.
Types of malvertising
Malvertising can take various forms to deliver malicious content through online advertisements. In this topic we have some malvertising examples, but it's important to note that malvertising is not limited to a single method or technique. Cybercriminals continuously evolve their tactics to bypass security measures and deliver their malicious payloads.
- Hidden inline frames
Inline frames are embedded HTML documents, such as web pages. Websites may feature inline frames that contain the content of other web pages. Hackers may use hidden inline frames to trick users into downloading malware from these other web pages. The inline frames may look like native ads, but they are actually embedded web pages that contain malware.
- Click fraud, such as fake ‘close’ buttons
Some malicious ads trick users into downloading malware by leveraging a fake “close” buttons. Most ads feature a “close” button. Malvertising still features an X in the corner, but clicking this X won’t close them. Instead, it will deploy malware onto the user’s device.
- Fake software updates
Malvertisements may prompt users to download fake software updates or security patches that are actually malware in disguise.

- Drive-by downloads
Drive-by downloads are often used for malvertising purposes. Drive-by downloads involve a user unknowingly downloading malware or malicious code.
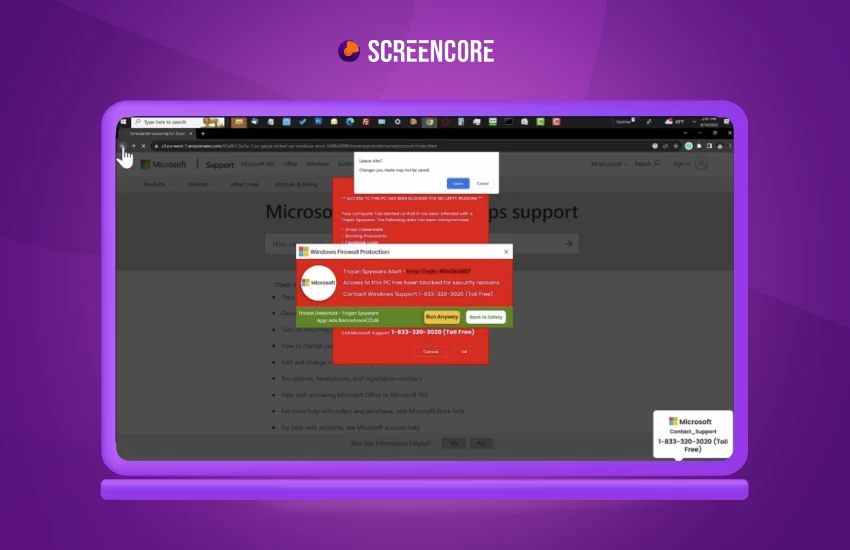
- Tech support scams
Malvertisers may display fake tech support pop-ups, warning users of non-existent security threats and urging them to call a fraudulent support hotline.
- Sneaky redirects
Another common type of malvertising is sneaky redirects. Nearly all ads on the internet point to another web page. Sneaky redirects involve tricking users into clicking an ad by sending them to a different web page other than what they expected. Users may assume that an ad points to a legitimate business web page. Clicking the ad, though, may redirect them to a different web page, such as a malicious web page that infects their device.
How to protect against malvertising?
It's crucial to take proactive measures to protect your website and users from malvertising. Here are steps you can take to safeguard your online platform:
Implement ad quality controls
Screencore implements strict quality controls and guidelines for the advertisements. This includes reviewing ad content, landing pages, and ensuring compliance with site's policies.
Consider an ad security partner
Screencore maintains a safe and secure advertising ecosystem and cooperates with The Media Trust (TMT), a leading force in the fight against malvertising.
Through our collaboration with TMT, we actively monitor and analyze every piece of digital advertising that Screencore represents. Their real-time scanning and verification processes keep us ahead of potential threats. With TMT’s vigilant eye and proactive approach, we can confidently provide our audience with safe and secure creative experiences.
Regularly update and patch
Keep your website's software, content management system, and plugins up to date. We regularly apply security patches and updates to reduce vulnerabilities that malvertisers may exploit.
Monitor ad delivery
Continuously monitor ad delivery on your website for any signs of malvertising. Be vigilant for unexpected redirects, pop-ups, or suspicious behavior.
Implement click tracking and reporting
Screencore provides a way for users to report suspicious or malicious ads. Implement click-tracking and reporting mechanisms so users can flag problematic ads.
Have a malvertising response plan
Our company has a clear and well-documented malvertising response plan. It includes steps to take in the event that a malicious ad is discovered, including removal and reporting to relevant authorities.
Stay informed
Keep up to date with the latest malvertising trends and threats. Being aware of evolving tactics can help you proactively protect your platform.

